Page 214 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 1
P. 214
CPS1282 Liu J. et al.
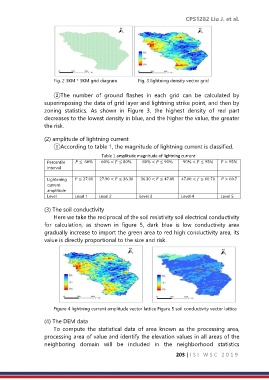
Fig. 2 3KM * 3KM grid diagram Fig. 3 lightning density vector grid
②The number of ground flashes in each grid can be calculated by
superimposing the data of grid layer and lightning strike point, and then by
zoning statistics. As shown in Figure 3, the highest density of red part
decreases to the lowest density in blue, and the higher the value, the greater
the risk.
(2) amplitude of lightning current
①According to table 1, the magnitude of lightning current is classified.
Table 1 amplitude magnitude of lightning current
Percentile ≤ 60% 60% < ≤ 80% 80% < ≤ 90% 90% < ≤ 95% > 95%
interval
Lightening ≤ 27.90 27.90 < ≤ 36.30 36.30 < ≤ 47.00 47.00 < ≤ 60.70 > 60.7
current
amplitude
Level Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5
(3) The soil conductivity
Here we take the reciprocal of the soil resistivity soil electrical conductivity
for calculation, as shown in figure 5, dark blue is low conductivity area
gradually increase to import the green area to red high conductivity area, its
value is directly proportional to the size and risk.
Figure 4 lightning current amplitude vector lattice Figure 5 soil conductivity vector lattice
(4) The DEM data
To compute the statistical data of area known as the processing area,
processing area of value and identify the elevation values in all areas of the
neighboring domain will be included in the neighborhood statistics
203 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9