Page 93 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 1
P. 93
IPS98 Luciana D. V. at al.
results calibrate the overly negative online reviews and underline the areas of
excellence of the airport.
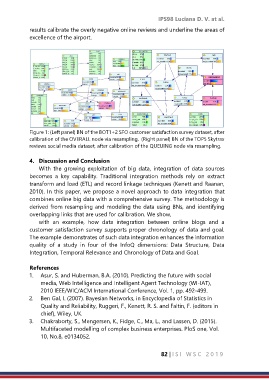
Figure 1: (Left panel) BN of the BOT1+2 SFO customer satisfaction survey dataset, after
calibration of the OVERALL node via resampling. (Right panel) BN of the TOP5 Skytrax
reviews social media dataset, after calibration of the QUEUING node via resampling.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
With the growing exploitation of big data, integration of data sources
becomes a key capability. Traditional integration methods rely on extract
transform and load (ETL) and record linkage techniques (Kenett and Raanan,
2010). In this paper, we propose a novel approach to data integration that
combines online big data with a comprehensive survey. The methodology is
derived from resampling and modeling the data using BNs, and identifying
overlapping links that are used for calibration. We show,
with an example, how data integration between online blogs and a
customer satisfaction survey supports proper chronology of data and goal.
The example demonstrates of such data integration enhances the information
quality of a study in four of the InfoQ dimensions: Data Structure, Data
Integration, Temporal Relevance and Chronology of Data and Goal.
References
1. Asur, S. and Huberman, B.A. (2010). Predicting the future with social
media, Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT),
2010 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference, Vol. 1, pp. 492-499.
2. Ben Gal, I. (2007). Bayesian Networks, in Encyclopedia of Statistics in
Quality and Reliability, Ruggeri, F., Kenett, R. S. and Faltin, F. (editors in
chief), Wiley, UK.
3. Chakraborty, S., Mengersen, K., Fidge, C., Ma, L., and Lassen, D. (2015).
Multifaceted modelling of complex business enterprises. PloS one, Vol.
10, No.8, e0134052.
82 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9