Page 226 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 4
P. 226
STS582 Júlia M. P. S.
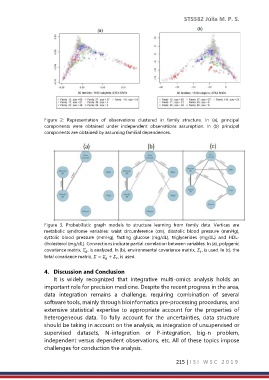
Figure 2: Representation of observations clustered in family structure. In (a), principal
components were obtained under independent observations assumption. In (b) principal
components are obtained by assuming familial dependences.
Figure 3. Probabilistic graph models to structure learning from family data. Vertices are
metabolic syndrome variables: waist circumference (cm), diastolic blood pressure (mmHg),
systolic blood pressure (mmHg), fasting glucose (mg/dL), triglycerides (mg/dL) and HDL-
cholesterol (mg/dL). Connections indicate partial correlation between variables. In (a), polygenic
covariance matrix, , is analyzed. In (b), environmental covariance matrix, , is used. In (c), the
total covariance matrix, = + , is used.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
It is widely recognized that integrative multi-omics analysis holds an
important role for precision medicine. Despite the recent progress in the area,
data integration remains a challenge, requiring combination of several
software tools, mainly through bioinformatics pre-processing procedures, and
extensive statistical expertise to appropriate account for the properties of
heterogeneous data. To fully account for the uncertainties, data structure
should be taking in account on the analysis, as integration of unsupervised or
supervised datasets, N-integration or P-integration, big-n problem,
independent versus dependent observations, etc. All of these topics impose
challenges for conduction the analysis.
215 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9