Page 207 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 1
P. 207
CPS1280 Willard Z. et al.
Kriging is a stochastic interpolation method which is used to map
unsampled locations using the available data sets. It is also known as Wiener-
Kolmogorov prediction (Robinson & Metternicht, 2003). Given a point 0, the
ordinary kriging estimator at 0 based on the data (i) = 1, … , is defined
as the linear unbiased estimator.
̂
( ) = ∑ ( ) (4)
=1
of ( )with minimum mean square prediction error. Where i ∈ ℝ is the
unknown weights corresponding with the influence of the variable ( ) in the
computation of ( ) (Bonaventura & Castruccio, 2005).
3. Results
The average monthly rainfall data was calculated based on the daily rainfall
data collected by South African weather service (SAWS) for the period 1980 to
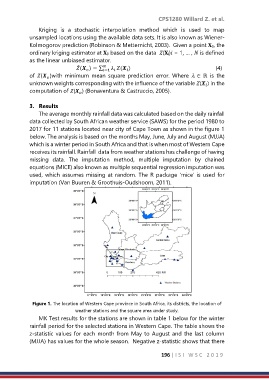
2017 for 11 stations located near city of Cape Town as shown in the figure 1
below. The analysis is based on the months May, June, July and August (MJJA)
which is a winter period in South Africa and that is when most of Western Cape
receives its rainfall. Rainfall data from weather stations has challenge of having
missing data. The imputation method, multiple imputation by chained
equations (MICE) also known as multiple sequential regression imputation was
used, which assumes missing at random. The R package ‘mice’ is used for
imputation (Van Buuren & Groothuis-Oudshoorn, 2011).
Figure 1. The location of Western Cape province in South Africa, its districts, the location of
weather stations and the square area under study.
MK Test results for the stations are shown in table 1 below for the winter
rainfall period for the selected stations in Western Cape. The table shows the
z-statistic values for each month from May to August and the last column
(MJJA) has values for the whole season. Negative z-statistic shows that there
196 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9