Page 242 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 1
P. 242
CPS1290 Sahda R. et al.
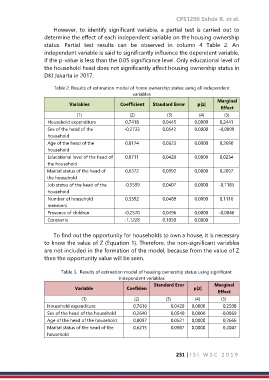
However, to identify significant variable, a partial test is carried out to
determine the effect of each independent variable on the housing ownership
status. Partial test results can be observed in column 4 Table 2. An
independent variable is said to significantly influence the dependent variable,
if the p-value is less than the 0.05 significance level. Only educational level of
the household head does not significantly affect housing ownership status in
DKI Jakarta in 2017.
Table 2. Results of estimation model of home ownership status using all independent
variables
Marginal
Variables Coefficient Standard Error p|z|
Effect
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Household expenditure 0,7418 0,0445 0,0000 0,2441
Sex of the head of the -0,2733 0,0542 0,0000 -0,0899
household
Age of the head of the 0,8174 0,0623 0,0000 0,2690
household
Educational level of the head of 0,0711 0,0420 0,0900 0,0234
the household
Marital status of the head of 0,6372 0,0992 0,0000 0,2097
the household
Job status of the head of the -0,3599 0,0407 0,0000 -0,1185
household
Number of household 0,3392 0,0489 0,0000 0,1116
members
Presence of children -0,2570 0,0496 0,0000 -0,0846
Constants -1,1228 0,1050 0,0000
To find out the opportunity for households to own a house, it is necessary
to know the value of Z (Equation 1). Therefore, the non-significant variables
are not included in the formation of the model, because from the value of Z
then the opportunity value will be seen.
Table 3. Results of estimation model of housing ownership status using significant
independent variables
Standard Eror Marginal
Variable Coefisien p|z|
Effect
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Household expenditure 0,7616 0,0429 0,0000 0,2508
Sex of the head of the household -0,2640 0,0540 0,0000 -0,0869
Age of the head of the household 0,8097 0,0621 0,0000 0,2666
Marital status of the head of the 0,6215 0,0987 0,0000 0,2047
household
231 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9