Page 208 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 3
P. 208
CPS1996 Ali Hebishi Kamel A. et al.
ratio of completed secondary education of individuals. Also it has high
effect of binary logistic regression of completed secondary education with
other independent variables such as gender of individuals, HH-size, place
of residence and mother education status according to results of the
model. That conclusion answers the second research question “Is THE
RELATION BETWEEN EDUCATION AND INCOME OF HOUSE HOLD?”
• From first and second analysis there is a relationship between income
inequality and education disparities. So when HH moves from under
secondary education to completed secondary education the average of
income increases to 57305.2 from 38952.48 LE. according to the model.
which means the increase in average income according to completed
secondary education compared to under secondary education is 18352.73
with 32.03%.
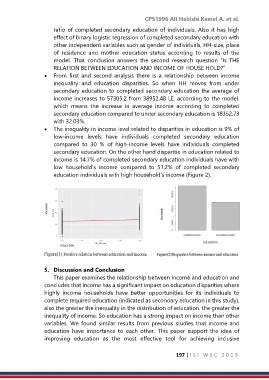
• The inequality in income level related to disparities in education is 9% of
low-income levels have individuals completed secondary education
compared to 30 % of high-income levels have individuals completed
secondary education. On the other hand disparitie in education related to
income is 14.7% of completed secondary education individuals have with
low household's income compared to 51.2% of completed secondary
education individuals with high household's income (Figure 2).
5. Discussion and Conclusion
This paper examines the relationship between income and education and
concludes that income has a significant impact on education disparities where
highly income households have better opportunities for its individuals to
complete required education (indicated as secondary education in this study),
also the greater the inequality in the distribution of education, the greater the
inequality of income. So education has a strong impact on income than other
variables. We found similar results from previous studies that income and
education have importance to each other. This paper support the idea of
improving education as the most effective tool for achieving inclusive
197 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9