Page 223 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 8
P. 223
CPS2256 Norzarita Samsudin
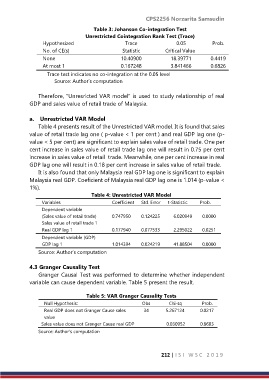
Table 3: Johanson Co-integration Test
Unrestricted Cointegration Rank Test (Trace)
Hypothesized Trace 0.05 Prob.
No. of CE(s) Statistic Critical Value
None 10.40900 18.39771 0.4419
At most 1 0.167248 3.841466 0.6826
Trace test indicates no co-integration at the 0.05 level
Source: Author’s computation
Therefore, “Unresricted VAR model” is used to study relationship of real
GDP and sales value of retail trade of Malaysia.
a. Unrestricted VAR Model
Table 4 presents result of the Unrestricted VAR model. It is found that sales
value of retail trade lag one ( p-value < 1 per cent ) and real GDP lag one (p-
value < 5 per cent) are significant to explain sales value of retail trade. One per
cent increase in sales value of retail trade lag one will result in 0.75 per cent
increase in sales value of retail trade. Meanwhile, one per cent increase in real
GDP lag one will result in 0.18 per cent increase in sales value of retail trade.
It is also found that only Malaysia real GDP lag one is significant to explain
Malaysia real GDP. Coeficient of Malaysia real GDP lag one is 1.014 (p-value <
1%).
Table 4: Unrestricted VAR Model
Variables Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob.
Dependent variable
(Sales value of retail trade) 0.747950 0.124225 6.020949 0.0000
Sales value of retail trade 1
Real GDP lag 1 0.177940 0.077533 2.295022 0.0251
Dependent variable (GDP)
GDP lag 1 1.014394 0.024219 41.88504 0.0000
Source: Author’s computation
4.3 Granger Causality Test
Granger Causal Test was performed to determine whether independent
variable can cause dependent variable. Table 5 present the result.
Table 5: VAR Granger Causality Tests
Null Hypothesis: Obs Chi-sq Prob.
Real GDP does not Granger Cause sales 34 5.267124 0.0217
value
Sales value does not Granger Cause real GDP 0.030952 0.8603
Source: Author’s computation
212 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9