Page 68 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 1
P. 68
IPS57 Joanne H.
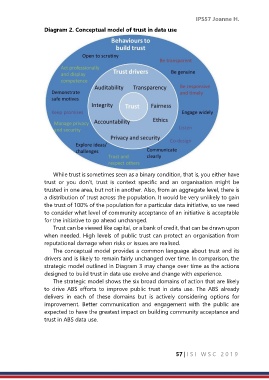
Diagram 2. Conceptual model of trust in data use
While trust is sometimes seen as a binary condition, that is, you either have
trust or you don’t, trust is context specific and an organisation might be
trusted in one area, but not in another. Also, from an aggregate level, there is
a distribution of trust across the population. It would be very unlikely to gain
the trust of 100% of the population for a particular data initiative, so we need
to consider what level of community acceptance of an initiative is acceptable
for the initiative to go ahead unchanged.
Trust can be viewed like capital, or a bank of credit, that can be drawn upon
when needed. High levels of public trust can protect an organisation from
reputational damage when risks or issues are realised.
The conceptual model provides a common language about trust and its
drivers and is likely to remain fairly unchanged over time. In comparison, the
strategic model outlined in Diagram 3 may change over time as the actions
designed to build trust in data use evolve and change with experience.
The strategic model shows the six broad domains of action that are likely
to drive ABS efforts to improve public trust in data use. The ABS already
delivers in each of these domains but is actively considering options for
improvement. Better communication and engagement with the public are
expected to have the greatest impact on building community acceptance and
trust in ABS data use.
57 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9