Page 253 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 253
STS489 Danielle J.R. et al.
(called “districts”) for Malawi, which consisted of 26 out of 28 districts for which
data was available; administrative level 2 (called “districts”) for mainland
Tanzania, which consisted of 176 out of 184 districts for which data was
available; and administrative level 1 (called “districts”) for Uganda, which
consisted of 121 out of 122 districts for which data is available; a total of 370
districts were considered.
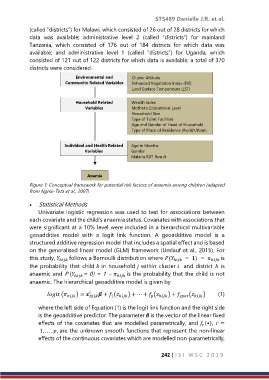
Environmental and Cluster Altitude
Community Related Variables Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI)
Land Surface Temperature (LST)
Household Related Wealth Index
Variables Mother’s Educational Level
Household Size
Type of Toilet Facilities
Age and Gender of Head of Household
Type of Place of Residence (Rural/Urban)
Individual and Health Related Age in Months
Variables Gender
Malaria RDT Result
Anemia
Figure 1: Conceptual framework for potential risk factors of anaemia among children (adapted
from Ngnie-Teta et al., 2007)
Statistical Methods
Univariate logistic regression was used to test for associations between
each covariate and the child’s anaemia status. Covariates with associations that
were significant at a 10% level were included in a hierarchical multivariable
geoadditive model with a logit link function. A geoadditive model is a
structured additive regression model that includes a spatial effect and is based
on the generalised linear model (GLM) framework (Umlauf et al., 2015). For
this study, ℎ follows a Bernoulli distribution where ( ℎ = 1) = ℎ is
the probability that child in household within cluster and district ℎ is
anaemic and P ( ℎ = 0) = 1 − ℎ is the probability that the child is not
anaemic. The hierarchical geoadditive model is given by
( ℎ ) = ′ ℎ + ( ℎ ) + ⋯ + ( ℎ ) + ( ℎ ) (1)
1
where the left side of Equation (1) is the logit link function and the right side
is the geoadditive predictor. The parameter β is the vector of the linear fixed
effects of the covariates that are modelled parametrically, and (•), =
1, . . . , , are the unknown smooth functions that represent the non-linear
effects of the continuous covariates which are modelled non-parametrically,
242 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9