Page 235 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 4
P. 235
STS582 Mariza de A.
3. Likelihood-based methods: Full information maximum likelihood, limited
information maximum likelihood, Bayesian methods, semi-parametric
methods.
4. Generalized Method of Moments: it is a semi-parametric estimator
designedas a more flexible form of 2SLS to deal with problems of
heteroscedasticity. (13)
3. Results
We presented the results oftwo studies using our Venous
Thromboembolism(VTE) data using MR to identify IV (height) and (BMI) for 2
studies (14,15).
Subject characteristics and their relationship with the genetic risk score (GRS)
for height in the Mayo VTE study (1994-2009)
characteristic Mean (SD) or % Full GRS (668 SNPs) * Restricted GRS (362
SNPs) *
2
2
Cases Controls R of GRS P R of GRS P
N=1143 N=1292
Standing height (cm) 172 (11) 171 (10) 0.075 <0.001 0.046 <0.001
Age (years) 55 (16) 56 (16) 0.002 0.09 0.003 0.04
Female sex 50 52 0.001 0.19 0.001 0.41
Body mass index (kg 31 (8) 29 (6) 0.000 0.80 0.001 0.30
-2
m )
Weight (kg) 94 (25) 84 (20) 0.018 <0.001 0.007 0.003
Prior 20 11 0.000 0.78 0.000 0.76
stroke/myocardial
infraction
Minnesota residency 45 55 0.001 0.23 0.003 0.05
SD, standard deviation; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
*Among controls only
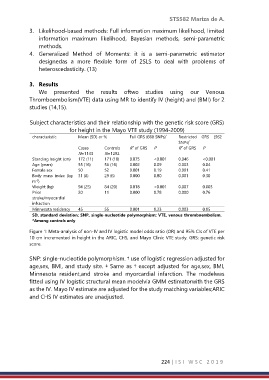
Figure 1: Meta-analysis of non-IV and IV logistic model odds ratio (OR) and 95% CIs of VTE per
10 cm incremented in height in the ARIC, CHS, and Mayo Clinic VTE study. GRS: genetic risk
score.
SNP: single-nucleotide polymorphism. † use of logistic regression adjusted for
age,sex, BMI, and study site. ‡ Same as † except adjusted for age,sex, BMI,
Minnesota resident,and stroke and myorcardial infarction. The modelwas
fitted using IV logistic structural mean modelvia GMM estimatorwith the GRS
as the IV. Mayo IV estimate are adjusted for the study matching variables;ARIC
and CHS IV estimates are unadjusted.
224 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9