Page 232 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 4
P. 232
STS582 Mariza de A.
variants. In summary MR study is a study that uses genetic variants that can
serve as a possible proxy for an environmentally modifiable exposure to make
causal inferences about the outcomes of the modifiable exposure. MR was
utilized in multiple studies to determine the causal relationships between
exposure and outcomes involving cancer, cardiovascular diseases, among
others.
The use of genotype to determine causal inference for the effect of a
modifiable (non-genetic) exposure on disease outcome is based on the
general theory of Instrumental Variables (IV) analysis where IV is a variable
associated with the outcome only though its robust association with an
intermediary variable, which is the exposure of interest.
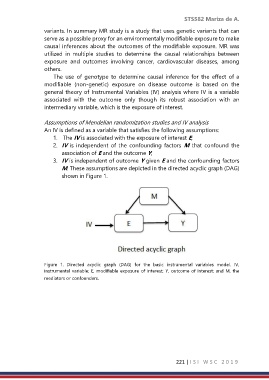
Assumptions of Mendelian randomization studies and IV analysis
An IV is defined as a variable that satisfies the following assumptions:
1. The IV is associated with the exposure of interest E;
2. IV is independent of the confounding factors M that confound the
association of E and the outcome Y;
3. IV is independent of outcome Y given E and the confounding factors
M. These assumptions are depicted in the directed acyclic graph (DAG)
shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Directed acyclic graph (DAG) for the basic instrumental variables model. IV,
instrumental variable; E, modifiable exposure of interest; Y, outcome of interest; and M, the
mediators or confounders.
221 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9