Page 109 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 5
P. 109
CPS1113 Madhu Mazumdar et al.
▪ Calendar time could be an IV, such as time to adopt a new treatment or
policy. One relevant example is the recent introduction of mandatory
participation in bundled payment programs for lower extremity joint
arthroplasty . Patients who had the procedure before this requirement by
8
definition cannot be exposed to these bundled payments; thus, calendar time
is highly associated with the program.
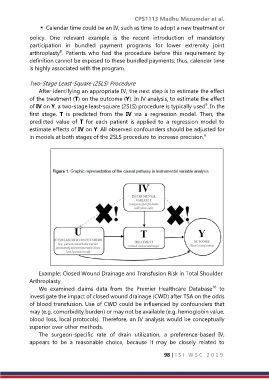
Two-Stage Least-Square (2SLS) Procedure
After identifying an appropriate IV, the next step is to estimate the effect
of the treatment (T) on the outcome (Y). In IV analysis, to estimate the effect
9
of IV on Y, a two-stage least-square (2SLS) procedure is typically used . In the
first stage, T is predicted from the IV via a regression model. Then, the
predicted value of T for each patient is applied to a regression model to
estimate effects of IV on Y. All observed confounders should be adjusted for
6
in models at both stages of the 2SLS procedure to increase precision.
Example: Closed Wound Drainage and Transfusion Risk in Total Shoulder
Arthroplasty
We examined claims data from the Premier Healthcare Database to
10
investigate the impact of closed wound drainage (CWD) after TSA on the odds
of blood transfusion. Use of CWD could be influenced by confounders that
may (e.g. comorbidity burden) or may not be available (e.g. hemoglobin value,
blood loss, local protocols). Therefore, an IV analysis would be conceptually
superior over other methods.
The surgeon-specific rate of drain utilization, a preference-based IV,
appears to be a reasonable choice, because it may be closely related to
98 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9