Page 56 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 8
P. 56
CPS2179 Giuliana Passamani et al.
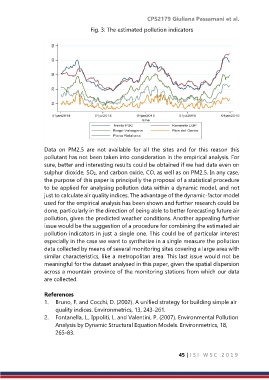
Fig. 3: The estimated pollution indicators
Data on PM2.5 are not available for all the sites and for this reason this
pollutant has not been taken into consideration in the empirical analysis. For
sure, better and interesting results could be obtained if we had data even on
sulphur dioxide, SO2, and carbon oxide, CO, as well as on PM2.5. In any case,
the purpose of this paper is principally the proposal of a statistical procedure
to be applied for analysing pollution data within a dynamic model, and not
just to calculate air quality indices. The advantage of the dynamic-factor model
used for the empirical analysis has been shown and further research could be
done, particularly in the direction of being able to better forecasting future air
pollution, given the predicted weather conditions. Another appealing further
issue would be the suggestion of a procedure for combining the estimated air
pollution indicators in just a single one. This could be of particular interest
especially in the case we want to synthetize in a single measure the pollution
data collected by means of several monitoring sites covering a large area with
similar characteristics, like a metropolitan area. This last issue would not be
meaningful for the dataset analysed in this paper, given the spatial dispersion
across a mountain province of the monitoring stations from which our data
are collected.
References
1. Bruno, F. and Cocchi, D. (2002). A unified strategy for building simple air
quality indices. Environmetrics, 13, 243-261.
2. Fontanella, L., Ippoliti, L. and Valentini, P. (2007). Environmental Pollution
Analysis by Dynamic Structural Equation Models. Environmetrics, 18,
265-83.
45 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9