Page 481 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 1
P. 481
IPS177 Jose-Maria S. G.
3. Trade repository data sharing
The survey reveals that data sharing is easier within central banks, and at
higher levels of aggregation. Central banks’ ability to share granular data with
external users is very constrained.
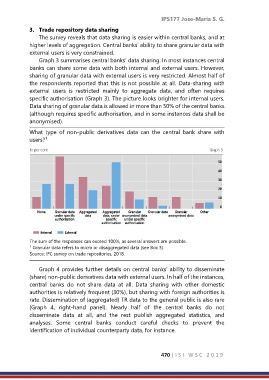
Graph 3 summarises central banks’ data sharing. In most instances central
banks can share some data with both internal and external users. However,
sharing of granular data with external users is very restricted. Almost half of
the respondents reported that this is not possible at all. Data-sharing with
external users is restricted mainly to aggregate data, and often requires
specific authorisation (Graph 3). The picture looks brighter for internal users.
Data sharing of granular data is allowed in more than 50% of the central banks
(although requires specific authorisation, and in some instances data shall be
anonymised).
What type of non-public derivatives data can the central bank share with
users?
1
The sum of the responses can exceed 100%, as several answers are possible.
1 Granular data refers to micro or disaggregated data (see Box 3).
Source: IFC survey on trade repositories, 2018.
Graph 4 provides further details on central banks’ ability to disseminate
(share) non-public derivatives data with external users. In half of the instances,
central banks do not share data at all. Data sharing with other domestic
authorities is relatively frequent (30%), but sharing with foreign authorities is
rate. Dissemination of (aggregated) TR data to the general public is also rare
(Graph 4, right-hand panel). Nearly half of the central banks do not
disseminate data at all, and the rest publish aggregated statistics, and
analyses. Some central banks conduct careful checks to prevent the
identification of individual counterparty data, for instance.
470 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9