Page 125 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 2
P. 125
IPS 188 G. P. Samanta
3.3 Correlation
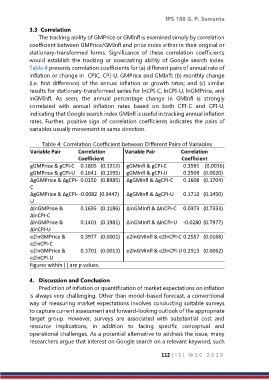
The tracking ability of GMPrice or GMInfl is examined simply by correlation
coefficient between GMPrice/GMInfl and price index either in their original or
stationary-transformed forms. Significance of these correlation coefficients
would establish the tracking or nowcasting ability of Google search index.
Table 4 presents correlation coefficients for (a) different pairs of annual rate of
inflation or change in CPIC, CPI-U, GMPrice and GMInfl; (b) monthly change
(i.e. first difference) of the annual inflation or growth rates; and (c) similar
results for stationary-transformed series for lnCPI-C, lnCPI-U, lnGMPrice, and
lnGMInfl. As seen, the annual percentage change in GMInfl is strongly
correlated with annual inflation rates based on both CPI-C and CPI-U,
indicating that Google search index GMInfl is useful in tracking annual inflation
rates. Further, positive sign of correlation coefficients indicates the pairs of
variables usually movement in same direction.
Table 4: Correlation Coefficient between Different Pairs of Variables
Variable Pair Correlation Variable Pair Correlation
Coefficient Coefficient
gGMPrice & gCPI-C 0.1805 (0.1212) gGMInfl & gCPI-C 0.3591 (0.0016)
gGMPrice & gCPI-U 0.1641 (0.1595) gGMInfl & gCPI-U 0.3509 (0.0020)
∆gGMPrice & ∆gCPI- 0.0150 (0.8985) ∆gGMInfl & ∆gCPI-C 0.1608 (0.1704)
C
∆gGMPrice & ∆gCPI- -0.0082 (0.9447) ∆gGMInfl & ∆gCPI-U 0.1710 (0.1450)
U
∆lnGMPrice & 0.1695 (0.1186) ∆lnGMInfl & ∆lnCPI-C 0.0373 (0.7333)
∆lnCPI-C
∆lnGMPrice & 0.1401 (0.1981) ∆lnGMInfl & ∆lnCPI-U -0.0280 (0.7977)
∆lnCPI-U
e2lnGMPrice & 0.3977 (0.0001) e2lnGMInfl & e2lnCPI-C 0.2557 (0.0168)
e2lnCPI-C
e2lnGMPrice & 0.3701 (0.0013) e2lnGMInfl & e2lnCPI-U 0.2913 (0.0062)
e2lnCPI-U
Figures within ( ) are p-values.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Prediction of inflation or quantification of market expectations on inflation
is always very challenging. Other than model-based forecast, a conventional
way of measuring market expectations involves conducting suitable surveys
to capture current assessment and forward-looking outlook of the appropriate
target group. However, surveys are associated with substantial cost and
resource implications, in addition to facing specific conceptual and
operational challenges. As a potential alternative to address the issue, many
researchers argue that interest on Google search on a relevant keyword, such
112 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9