Page 37 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 37
STS452 Yang C. et al.
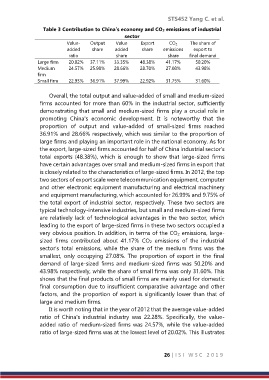
Table 3 Contribution to China’s economy and CO 2 emissions of industrial
sector
Value- Output Value Export CO 2 The share of
added share added share emissions export to
ratio share share final demand
Large firm 20.02% 37.11% 33.35% 48.38% 41.17% 50.20%
Medium 24.57% 25.98% 28.66% 28.70% 27.08% 43.98%
firm
Small firm 22.93% 36.91% 37.99% 22.92% 31.75% 31.60%
Overall, the total output and value-added of small and medium-sized
firms accounted for more than 60% in the industrial sector, sufficiently
demonstrating that small and medium-sized firms play a crucial role in
promoting China's economic development. It is noteworthy that the
proportion of output and value-added of small-sized firms reached
36.91% and 28.66% respectively, which was similar to the proportion of
large firms and playing an important role in the national economy. As for
the export, large-sized firms accounted for half of China industrial sector’s
total exports (48.38%), which is enough to show that large-sized firms
have certain advantages over small and medium-sized firms in export that
is closely related to the characteristics of large-sized firms. In 2012, the top
two sectors of export scale were telecommunication equipment, computer
and other electronic equipment manufacturing and electrical machinery
and equipment manufacturing, which accounted for 26.99% and 9.75% of
the total export of industrial sector, respectively. These two sectors are
typical technology-intensive industries, but small and medium-sized firms
are relatively lack of technological advantages in the two sector, which
leading to the export of large-sized firms in these two sectors occupied a
very obvious position. In addition, in terms of the CO2 emissions, large-
sized firms contributed about 41.17% CO2 emissions of the industrial
sector’s total emissions, while the share of the medium firms was the
smallest, only occupying 27.08%. The proportion of export in the final
demand of large-sized firms and medium-sized firms was 50.20% and
43.98% respectively, while the share of small firms was only 31.60%. This
shows that the final products of small firms are mainly used for domestic
final consumption due to insufficient comparative advantage and other
factors, and the proportion of export is significantly lower than that of
large and medium firms.
It is worth noting that in the year of 2012 that the average value-added
ratio of China's industrial industry was 22.28%. Specifically, the value-
added ratio of medium-sized firms was 24.57%, while the value-added
ratio of large-sized firms was at the lowest level of 20.02%. This illustrates
26 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9