Page 400 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 400
STS507 Katherine Jenny T. et al.
slowly, with the acquisition of a processing environment and historical data
sets. Subject matter experts extracted the EC test data from industries
provided by the classification experts. They also provided classification rules
for donor records (whose values can be used for imputation) and recipient
records (need an imputed value), thus ensuring that industry-specific “must-
product” rules would be enforced by any imputation method. The
classification experts provided industries whose product distributions were
expected to remain largely the same under NAPCS. Even so, the historical
product data were not expected to be perfect predictors of the 2017 product
data due to numerous collection changes from the 2012 EC.
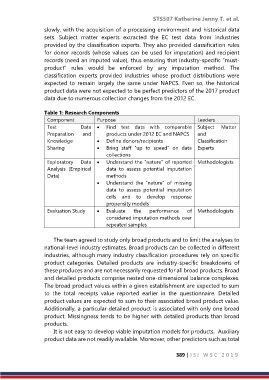
Table 1: Research Components
Component Purpose Leaders
Test Data Find test data with comparable Subject Matter
Preparation and products under 2012 EC and NAPCS and
Knowledge Define donors/recipients Classification
Sharing Bring staff “up to speed” on data Experts
collections
Exploratory Data Understand the “nature” of reported Methodologists
Analysis (Empirical data to assess potential imputation
Data) methods
Understand the “nature” of missing
data to assess potential imputation
cells and to develop response
propensity models
Evaluation Study Evaluate the performance of Methodologists
considered imputation methods over
repeated samples
The team agreed to study only broad products and to limit the analyses to
national-level industry estimates. Broad products can be collected in different
industries, although many industry classification procedures rely on specific
product categories. Detailed products are industry-specific breakdowns of
these produces and are not necessarily requested for all broad products. Broad
and detailed products comprise nested one-dimensional balance complexes.
The broad product values within a given establishment are expected to sum
to the total receipts value reported earlier in the questionnaire. Detailed
product values are expected to sum to their associated broad product value.
Additionally, a particular detailed product is associated with only one broad
product. Missingness tends to be higher with detailed products than broad
products.
It is not easy to develop viable imputation models for products. Auxiliary
product data are not readily available. Moreover, other predictors such as total
389 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9