Page 191 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 2
P. 191
CPS1820 Shuichi S.
3. Cancer Gene Diagnosis
We analyze all SMs by statistical methods because all SMs are small
samples. However, we cannot obtain good results. Only RIP and H-SVM can
discriminate all SMs correctly. We realize RipDSs, and H-SVM discriminant
scores (HsvmDSs) express the signal of microarrays. Thus, we make signal data
using RipDSs and H-SVM DSs instead of genes. If we analyze these signal data
by Ward cluster, it can separate two classes into two clusters. Next, we analyze
signal data by PCA, and we propose the malignancy index by PCA in addition
to RipDSs and HsvmDSs [10-11]. Moreover, we develop RatioSV to evaluate
SM and BGS that is vital second statistics in addition to MNM for
LSDdiscrimination. Now, we open the new frontier of cancer gene diagnosis
[10-12].
a. Evaluation of Alon’s SMs
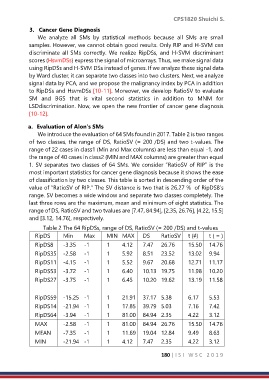
We introduce the evaluation of 64 SMs found in 2017. Table 2 is two ranges
of two classes, the range of DS, RatioSV (= 200 /DS) and two t-values. The
range of 22 cases in class1 (Min and Max columns) are less than equal -1, and
the range of 40 cases in class2 (MIN and MAX columns) are greater than equal
1. SV separates two classes of 64 SMs. We consider “RatioSV of RIP” is the
most important statistics for cancer gene diagnosis because it shows the ease
of classification by two classes. This table is sorted in descending order of the
value of “RatioSV of RIP.” The SV distance is two that is 26.27 % of RipDS8's
range. SV becomes a wide window and separate two classes completely. The
last three rows are the maximum, mean and minimum of eight statistics. The
range of DS, RatioSV and two tvalues are [7.47, 84.94], [2.35, 26.76], [4.22, 15.5]
and [3.12, 14.76], respectively.
Table 2 The 64 RipDSs, range of DS, RatioSV (= 200 /DS) and t-values
RipDS Min Max MIN MAX DS RatioSV t (≠) t ( = )
RipDS8 -3.35 -1 1 4.12 7.47 26.76 15.50 14.76
RipDS35 -2.58 -1 1 5.92 8.51 23.52 13.02 9.94
RipDS11 -4.15 -1 1 5.52 9.67 20.68 12.71 11.17
RipDS53 -3.72 -1 1 6.40 10.13 19.75 11.98 10.20
RipDS27 -3.75 -1 1 6.45 10.20 19.62 13.19 11.58
RipDS59 -15.25 -1 1 21.91 37.17 5.38 6.17 5.53
RipDS14 -21.94 -1 1 17.85 39.79 5.03 7.16 7.42
RipDS64 -3.94 -1 1 81.00 84.94 2.35 4.22 3.12
MAX -2.58 -1 1 81.00 84.94 26.76 15.50 14.76
MEAN -7.35 -1 1 11.69 19.04 12.84 9.49 8.63
MIN -21.94 -1 1 4.12 7.47 2.35 4.22 3.12
180 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9