Page 239 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 3
P. 239
CPS2003 Bruno de S. et al.
order random walk penalty with 20 inner knots. For the spatial components, a
Gaussian Markov random field is used for the structured effects, (.), and an
iid Gaussian random effects for the unstructured effects, (.) [10]. To take
into account the excess of zeros and possible overdispersion of the data, a
zero-inflated negative binomial distribution for the response variable was
assumed [11]. Inference results are obtained considering a FB approach.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Descriptive analysis
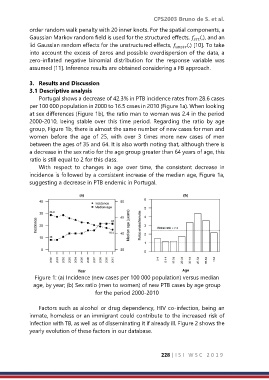
Portugal shows a decrease of 42.3% in PTB incidence rates from 28.6 cases
per 100 000 population in 2000 to 16.5 cases in 2010 (Figure 1a). When looking
at sex differences (Figure 1b), the ratio man to woman was 2.4 in the period
2000-2010, being stable over this time period. Regarding the ratio by age
group, Figure 1b, there is almost the same number of new cases for men and
women before the age of 25, with over 3 times more new cases of men
between the ages of 35 and 64. It is also worth noting that, although there is
a decrease in the sex ratio for the age group greater than 64 years of age, this
ratio is still equal to 2 for this class.
With respect to changes in age over time, the consistent decrease in
incidence is followed by a consistent increase of the median age, Figure 1a,
suggesting a decrease in PTB endemic in Portugal.
Figure 1: (a) Incidence (new cases per 100 000 population) versus median
age, by year; (b) Sex ratio (men to women) of new PTB cases by age group
for the period 2000-2010
Factors such as alcohol or drug dependency, HIV co-infection, being an
inmate, homeless or an immigrant could contribute to the increased risk of
infection with TB, as well as of disseminating it if already ill. Figure 2 shows the
yearly evolution of these factors in our database.
228 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9