Page 32 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 3
P. 32
CPS1934 Atikur R. K. et al.
Category 3: This category is supposed to has a lower degree of RTI episodes
and can be defined as ( 4 < () ≤ 6 ) ∪ ( () ≤ 4 ∩
() > 2 ), that is, this category can be defined based on defined rolling
statistics as ( 4 < (|) ≤ 6 ) ∪ ( (|) ≤ 4 ∩ (|) > 2 ).
ℎ ℎ
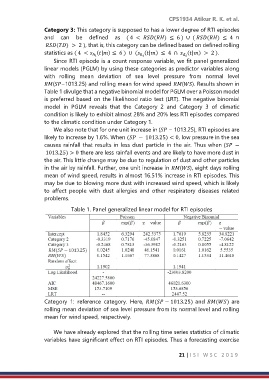
Since RTI episode is a count response variable, we fit panel generalized
linear models (PGLM) by using these categories as predictor variables along
with rolling mean deviation of sea level pressure from normal level
(−1013.25) and rolling mean for wind speed (). Results shown in
Table 1 divulge that a negative binomial model for PGLM over a Poisson model
is preferred based on the likelihood ratio test (LRT). The negative binomial
model in PGLM reveals that the Category 2 and Category 3 of climatic
condition is likely to exhibit almost 28% and 20% less RTI episodes compared
to the climatic condition under Category 1.
We also note that for one unit increase in ( − 1013.25), RTI episodes are
likely to increase by 1.6%. When ( − 1013.25) < 0, low pressure in the sea
causes rainfall that results in less dust particle in the air. Thus when ( −
1013.25) > 0 there are less rainfall events and are likely to have more dust in
the air. This little change may be due to regulation of dust and other particles
in the air by rainfall. Further, one unit increase in (), eight days rolling
mean of wind speed, results in almost 16.51% increase in RTI episodes. This
may be due to blowing more dust with increased wind speed, which is likely
to affect people with dust allergies and other respiratory diseases related
problems.
Table 1. Panel generalized linear model for RTI episodes
Category 1: reference category. Here, ( − 1013.25) and () are
rolling mean deviation of sea level pressure from its normal level and rolling
mean for wind speed, respectively.
We have already explored that the rolling time series statistics of climatic
variables have significant effect on RTI episodes. Thus a forecasting exercise
21 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9