Page 104 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 8
P. 104
CPS2205 Abdul Aziz A. Rahaman et al.
2.2.4 The Ordinal Logit Model
The following notation would employed in the model. Let = Pr ( = 2)
2
denotes the probability that the ith individual's outcome belongs to the
second class; More generally, = Pr( = ) denotes the probability that the
ith individual's outcome belongs to the kth class. On the other hand when the
categories are ordered to assume that the log odds of ≥ is linearly linked
with the predictor variables. The model is given by
log ( +⋯+ ) = 0 + (6)
1+⋯+ −1
Thus, we still have to estimate K 1 intercepts, but only p linear effects, where p is
the number of explanatory variables (note that + − 1 < ( − 1)( + 1) >
2.
2.2.5 Goodness of Fit Test for Structural Equation Model
A large class of omnibus tests exists for determining overall model fit. The
χ2 statistic is often used, for which the null hypothesis indicates how close the
default model is to the data set used.
2.2.6 Goodness-of-Fit Test for Ordinal Logit Model
From the observed and expected frequencies, the usual Pearson and
Deviance goodness-of-fit measures can be computed. The Pearson goodness-
of-fit statistic is
2
2
= ΣΣ ( − ) (7)
3. Result
Asymptotically distribution free method was adopted for parameter
estimation to justify data set used. Measurement model and structural model
test were used to test fitness of the model.
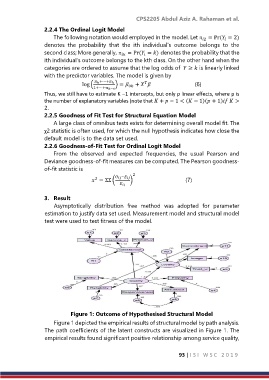
Figure 1: Outcome of Hypothesised Structural Model
Figure 1 depicted the empirical results of structural model by path analysis.
The path coefficients of the latent constructs are visualized in Figure 1. The
empirical results found significant positive relationship among service quality,
93 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9