Page 101 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 101
STS463 Siti Asiah A. et al.
achievement of full coverage. Third, is minimization of measurement errors
and the final steps is balancing.
ILO describes two approaches in compiling labour account which are
cross-sectional and longitudinal. Cross-sectional approach involves
confrontation and reconciliation of key labour market measure. Longitudinal
approach incorporates changes to population and labour force via births,
deaths and net migration (Buhmann et. al, 2002).
Australia, Denmark, the Netherland and Switzerland have followed these
approaches in developing a labour account system in their respective
countries. Australia and the Netherland adopt cross-sectional approach while
Denmark and Switzerland adopt both cross-sectional and longitudinal
approaches
Australia
The Australian Labour Account framework has been designed aligns with
United Nations System of National Accounts as applied in Australian System
of National Accounts (ASNA). This framework consists of four quadrants: Jobs,
Persons, Volume and Payments that covers all types of employment including
employees, self-employed and contributing family workers (Australian Labour
Account, 2018). The main identity relationship can be defined as follows:
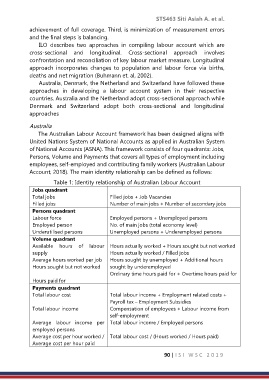
Table 1: Identity relationship of Australian Labour Account
Jobs quadrant
Total jobs Filled jobs + Job Vacancies
Filled jobs Number of main jobs + Number of secondary jobs
Persons quadrant
Labour force Employed persons + Unemployed persons
Employed person No. of main jobs (total economy level)
Underutilised persons Unemployed persons + Underemployed persons
Volume quadrant
Available hours of labour Hours actually worked + Hours sought but not worked
supply Hours actually worked / Filled jobs
Average hours worked per job Hours sought by unemployed + Additional hours
Hours sought but not worked sought by underemployed
Ordinary time hours paid for + Overtime hours paid for
Hours paid for
Payments quadrant
Total labour cost Total labour income + Employment related costs +
Payroll tax – Employment Subsidies
Total labour income Compensation of employees + Labour income from
self-employment
Average labour income per Total labour income / Employed persons
employed persons
Average cost per hour worked / Total labour cost / (Hours worked / Hours paid)
Average cost per hour paid
90 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9