Page 355 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 355
STS498 Wei-Yin L.
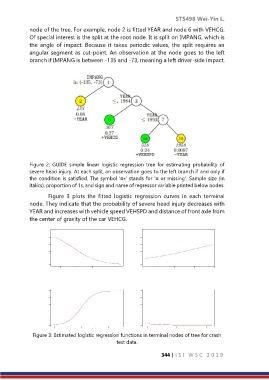
node of the tree. For example, node 2 is fitted YEAR and node 6 with VEHCG.
Of special interest is the split at the root node. It is split on IMPANG, which is
the angle of impact. Because it takes periodic values, the split requires an
angular segment as cut-point. An observation at the node goes to the left
branch if IMPANG is between -135 and -73, meaning a left driver-side impact.
Figure 2: GUIDE simple linear logistic regression tree for estimating probability of
severe head injury. At each split, an observation goes to the left branch if and only if
the condition is satisfied. The symbol ‘≤∗’ stands for ‘≤ or missing’. Sample size (in
italics), proportion of 1s, and sign and name of regressor variable printed below nodes.
Figure 3 plots the fitted logistic regression curves in each terminal
node. They indicate that the probability of severe head injury decreases with
YEAR and increases with vehicle speed VEHSPD and distance of front axle from
the center of gravity of the car VEHCG.
Figure 3: Estimated logistic regression functions in terminal nodes of tree for crash
test data.
344 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9