Page 354 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 354
STS498 Wei-Yin L.
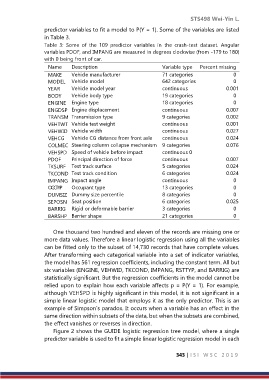
predictor variables to fit a model to P(Y = 1). Some of the variables are listed
in Table 3.
Table 3: Some of the 109 predictor variables in the crash-test dataset. Angular
variables PDOF, and IMPANG are measured in degrees clockwise (from -179 to 180)
with 0 being front of car.
Name Description Variable type Percent missing
MAKE Vehicle manufacturer 71 categories 0
MODEL Vehicle model 642 categories 0
YEAR Vehicle model year continuous 0.001
BODY Vehicle body type 19 categories 0
ENGINE Engine type 18 categories 0
ENGDSP Engine displacement continuous 0.007
TRANSM Transmission type 9 categories 0.002
VEHTWT Vehicle test weight continuous 0.001
VEHWID Vehicle width continuous 0.027
VEHCG Vehicle CG distance from front axle continuous 0.024
COLMEC Steering column collapse mechanism 9 categories 0.076
VEHSPD Speed of vehicle before impact continuous 0
PDOF Principal direction of force continuous 0.007
TKSURF Test track surface 5 categories 0.024
TKCOND Test track condition 6 categories 0.024
IMPANG Impact angle continuous 0
OCCTYP Occupant type 13 categories 0
DUMSIZ Dummy size percentile 8 categories 0
SEPOSN Seat position 6 categories 0.025
BARRIG Rigid or deformable barrier 3 categories 0
BARSHP Barrier shape 21 categories 0
One thousand two hundred and eleven of the records are missing one or
more data values. Therefore a linear logistic regression using all the variables
can be fitted only to the subset of 14,730 records that have complete values.
After transforming each categorical variable into a set of indicator variables,
the model has 561 regression coefficients, including the constant term. All but
six variables (ENGINE, VEHWID, TKCOND, IMPANG, RSTTYP, and BARRIG) are
statistically significant. But the regression coefficients in the model cannot be
relied upon to explain how each variable affects p = P(Y = 1). For example,
although VEHSPD is highly significant in this model, it is not significant in a
simple linear logistic model that employs it as the only predictor. This is an
example of Simpson’s paradox. It occurs when a variable has an effect in the
same direction within subsets of the data, but when the subsets are combined,
the effect vanishes or reverses in direction.
Figure 2 shows the GUIDE logistic regression tree model, where a single
predictor variable is used to fit a simple linear logistic regression model in each
343 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9