Page 48 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 2
P. 48
CPS1416 Jungtaek O. et al.
Finally, these five estimators are compared using the comparison statistics
which are Bias, Absolute bias and Root mean squared error(RMSE) defined by
1
2
1 () () 1 () () 2
̂
̂
Bias: ∑ (Y ̅ − Y ̅ ) , RMSE: { ∑ (Y ̅ − Y ̅ ) }
=1 =1
Where the number of iteration, R is 5,000. For reducing the specific
population effect, we generate population data with different seed for each
( )
iteration. Therefore the notation of is used for th population mean.
4.2 Simulation result
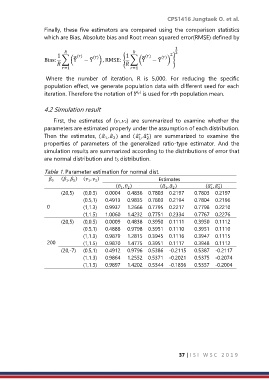
First, the estimates of (1,2) are summarized to examine whether the
parameters are estimated properly under the assumption of each distribution.
Then the estimates, (̂ , ̂ ) and (̂ , ̂ ) are summarized to examine the
∗
∗
1
2
2
1
properties of parameters of the generalized ratio-type estimator. And the
simulation results are summarized according to the distributions of error that
are normal distribution and t5 distribution.
Table 1. Parameter estimation for normal dist.
( , ) ( , ) Estimates
1
2
2
1
0
(̂ , ̂ ) (̂ , ̂ ) (̂ , ̂ )
∗
∗
1
2
1
1
2
2
(20,5) (0,0.5) 0.0004 0.4836 0.7803 0.2197 0.7803 0.2197
(0.5,1) 0.4913 0.9835 0.7803 0.2194 0.7804 0.2196
0 (1,1.3) 0.9937 1.2666 0.7795 0.2217 0.7798 0.2210
(1,1.5) 1.0060 1.4232 0.7751 0.2334 0.7767 0.2276
(20,5) (0,0.5) 0.0009 0.4838 0.3950 0.1111 0.3950 0.1112
(0.5,1) 0.4888 0.9798 0.3951 0.1110 0.3951 0.1110
(1,1.3) 0.9879 1.2815 0.3945 0.1116 0.3947 0.1115
200 (1,1.5) 0.9870 1.4775 0.3951 0.1117 0.3948 0.1112
(20,-7) (0.5,1) 0.4912 0.9796 0.5386 -0.2115 0.5387 -0.2117
(1,1.3) 0.9864 1.2552 0.5371 -0.2021 0.5375 -0.2074
(1,1.5) 0.9897 1.4202 0.5344 -0.1856 0.5357 -0.2004
37 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9