Page 148 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 4
P. 148
CPS2160 Aye Aye Khin et al.
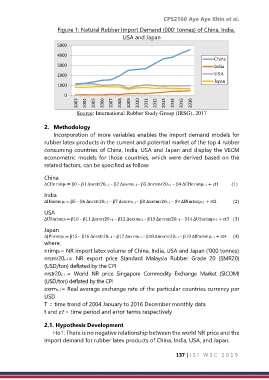
Figure 1: Natural Rubber Import Demand (000’ tonnes) of China, India,
USA and Japan
5000
4000
China
3000 India
2000 USA
Japan
1000
0
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
Source: International Rubber Study Group (IRSG), 2017
2. Methodology
Incorporation of more variables enables the import demand models for
rubber latex products in the current and potential market of the top 4 rubber
consuming countries of China, India, USA and Japan and display the VECM
econometric models for those countries, which were derived based on the
related factors, can be specified as follow:
China
∆CHnrimpt = β0 – β1 ∆nrstr20t-1 – β2 ∆exrmt-1 – β3 ∆nrsmr20t-1 – β4 ∆CHnrimpt-1 + εt1 (1)
India
∆INnrimpt = β5 – β6 ∆nrstr20t-1 – β7 ∆exrmt-1 – β8 ∆nrsmr20t-1 – β9 ∆INnrimpt-1 + εt2 (2)
USA
∆USnrimpt = β10 – β11 ∆nrstr20t-1 – β12 ∆exrmt-1 – β13 ∆nrsmr20t-1 – β14 ∆USnrimpt-1 + εt3 (3)
Japan
∆JPnrimpt = β15 – β16 ∆nrstr20t-1 – β17 ∆exrmt-1 – β18 ∆nrsmr20t-1 – β19 ∆JPnrimpt-1 + εt4 (4)
where,
nrimpt= NR import latex volume of China, India, USA and Japan (‘000 tonnes)
nrsmr20t-1= NR export price Standard Malaysia Rubber Grade 20 (SMR20)
(USD/ton) deflated by the CPI
nrstr20t-1 = World NR price Singapore Commodity Exchange Market (SICOM)
(USD/ton) deflated by the CPI
exrmt-1= Real average exchange rate of the particular countries currency per
USD
T = time trend of 2004 January to 2016 December monthly data
t and εt = time period and error terms respectively
2.1. Hypothesis Development
Ho1: There is no negative relationship between the world NR price and the
import demand for rubber latex products of China, India, USA, and Japan.
137 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9