Page 86 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 2
P. 86
IPS184 Kimiaki S. et al.
sometimes used as a proxy [Chart 9] Relationship between (a) a
variable for the amount of cross- differential between international
currency funding - funding by claims and liabilities and (b) the
foreign exchange (FX) swaps and amount of cross-currency funding
foreign currency swaps -- in
the context of U.S. dollar
funding. With regard to their
positions on a trust-account
basis, however, banks
themselves do not use FX
swaps or foreign currency
swaps for foreign currency
funding in many of such positions. The examples include positions in which
institutional investors, such as pension funds, sell Japanese yen to buy foreign
currencies, thereby investing them in foreign debt securities. Thus, there is a
possibility that (1) taking the differential between the banking-and-trust-
account-based international claims and liabilities held by Japanese banks,
which include the aforementioned
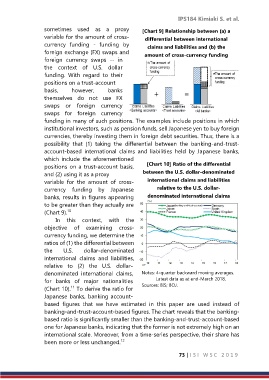
positions on a trust-account basis, [Chart 10] Ratio of the differential
and (2) using it as a proxy between the U.S. dollar-denominated
variable for the amount of cross- international claims and liabilities
currency funding by Japanese relative to the U.S. dollar-
banks, results in figures appearing denominated international claims
to be greater than they actually are
10
(Chart 9).
In this context, with the
objective of examining cross-
currency funding, we determine the
ratios of (1) the differential between
the U.S. dollar-denominated
international claims and liabilities,
relative to (2) the U.S. dollar-
denominated international claims, Notes: 4-quarter backward moving averages.
for banks of major nationalities Latest data as at end-March 2018.
11
(Chart 10). To derive the ratio for Sources: BIS; BOJ.
Japanese banks, banking account-
based figures that we have estimated in this paper are used instead of
banking-and-trust-account-based figures. The chart reveals that the banking-
based ratio is significantly smaller than the banking-and-trust-account-based
one for Japanese banks, indicating that the former is not extremely high on an
international scale. Moreover, from a time-series perspective, their share has
been more or less unchanged. 12
73 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9