Page 55 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 1
P. 55
STS364 Maria F.
nationally comparable education statistics. The UNESCO Institute for Statistics
and UNESCO-OECD-Eurostat (UOE) data collection programs, as well as
education statistics of UNESCO member states are collected according to the
suggested standards. Education programs and qualifications are organized by
education levels and fields. ISCED level reflects the degree of complexity and
specialization of education program content. Statistics on educational
programs provides information on the links between inputs (entrants into the
system), the process (participation) and the output (the qualification). Due to
this approach the qualification becomes the sign that the program graduate
possesses the level of professional skills enough to start professional career.
As we are interested in labour market analysis, the focus of our research is
methodology used to collect the data on tertiary education that includes both
academic and vocational (professional) education. The main actors in tertiary
education sector responsible for the professional training of human capital are
institutions and companies providing formal, non-formal education and
informal learning service to population. Formal education is provided by
public organizations and recognized private bodies. Vocational education is
often recognized as a part of formal education system. Programs that take
place partly in the workplace are also considered as formal education if they
lead to a qualification recognized by national education authorities.
Apprenticeships – programs provided in cooperation between educational
institutions and employers.
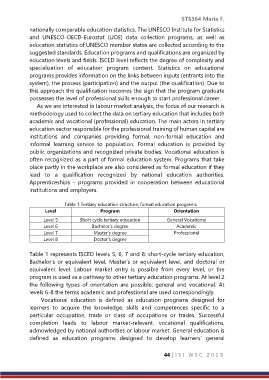
Table 1 Tertiary education structure, formal education programs
Level Program Orientation
Level 5 Short cycle tertiary education General Vocational
Level 6 Bachelor’s degree Academic
Level 7 Master’s degree Professional
Level 8 Doctor’s degree
Table 1 represents ISCED levels 5, 6, 7 and 8: short-cycle tertiary education,
Bachelor’s or equivalent level, Master’s or equivalent level, and doctoral or
equivalent level. Labour market entry is possible from every level, or the
program is used as a pathway to other tertiary education programs. At level 2
the following types of orientation are possible: general and vocational. At
levels 6-8 the terms academic and professional are used correspondingly.
Vocational education is defined as education programs designed for
learners to acquire the knowledge, skills and competences specific to a
particular occupation, trade or class of occupations or trades. Successful
completion leads to labour market-relevant, vocational qualifications,
acknowledged by national authorities or labour market. General education is
defined as education programs designed to develop learners’ general
44 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9