Page 162 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 162
STS474 Yoshihiro Y.
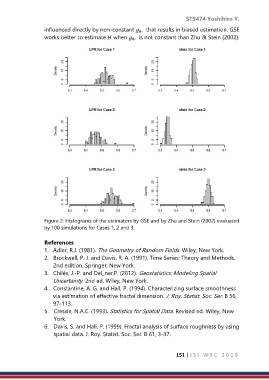
influenced directly by non-constant , that results in biased estimation. GSE
0
works better to estimate when , is not constant than Zhu & Stein (2002).
0
Figure 2: Histograms of the estimators by GSE and by Zhu and Stein (2002) evaluated
by 100 simulations for Cases 1, 2 and 3.
References
1. Adler, R.J. (1981). The Geometry of Random Fields. Wiley, New York.
2. Brockwell, P. J. and Davis, R. A. (1991). Time Series: Theory and Methods.
2nd edition. Springer, New York.
3. Chilés, J.-P. and Del_ner,P. (2012). Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial
Uncertainty. 2nd ed. Wiley, New York.
4. Constantine, A. G. and Hall, P. (1994). Characterizing surface smoothness
via estimation of effective fractal dimension. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B 56,
97-113.
5. Cressie, N.A.C. (1993). Statistics for Spatial Data. Revised ed. Wiley, New
York.
6. Davis, S. and Hall, P. (1999). Fractal analysis of surface roughness by using
spatial data. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B 61, 3-37.
151 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9