Page 396 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 3
P. 396
STS551 Stephen Wu et al.
typical Bayesian inference using these priors for all the corresponding
likelihoods, we will be able to obtain the following posterior:
(3)
If we can obtain estimation of the evidence term ( | ), we will be able to apply
the importance sampling method to estimate the integrals, i.e., an estimate of the
()
⃗⃗
important term of (| , ) by setting the proposals ( ) = ( | , ):
(4)
Because it is very common to first perform Bayesian inference on each data set
to get a rough understanding of the problem, this approximation method for
hierarchical Bayesian modeling can be seen as a very efficient post-processing that
recycle the samples drawn during those Bayesian inferences.
3. Results
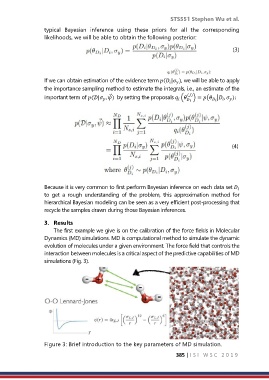
The first example we give is on the calibration of the force fields in Molecular
Dynamics (MD) simulations. MD is computational method to simulate the dynamic
evolution of molecules under a given environment. The force field that controls the
interaction between molecules is a critical aspect of the predictive capabilities of MD
simulations (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: Brief introduction to the key parameters of MD simulation.
385 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9