Page 23 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 4
P. 23
STS556 Nitin Kumar et al.
compared to more expensive forms of credit (Myers and Majluf, 1984).
Liquidity of firm as captured by current ratio is significant and positive. Higher
liquidity affords higher trade credit liability to a firm. The finding is consistent
as per Bougheas et al. (2009) and Vaidya (2011). Amongst macro indicators
higher interest rate is having a positive influence on account payables. Higher
rates narrow down the rate gap between formal sources of credit and trade
credit leading to greater usage of trade credit that is relatively convenient.
However, the role of both inflation and growth rate is negative dependent
variable.
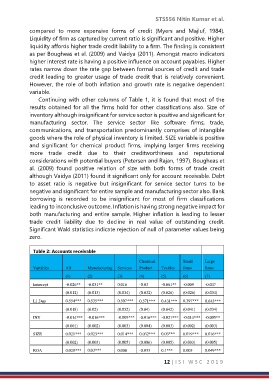
Continuing with other columns of Table 1, it is found that most of the
results obtained for all the firms hold for other classifications also. Size of
inventory although insignificant for service sector is positive and significant for
manufacturing sector. The service sector like software firms, trade,
communications, and transportation predominantly comprises of intangible
goods where the role of physical inventory is limited. SIZE variable is positive
and significant for chemical product firms, implying larger firms receiving
more trade credit due to their creditworthiness and reputational
considerations with potential buyers (Petersen and Rajan, 1997). Bougheas et
al. (2009) found positive relation of size with both forms of trade credit
although Vaidya (2011) found it significant only for account receivable. Debt
to asset ratio is negative but insignificant for service sector turns to be
negative and significant for entire sample and manufacturing sector also. Bank
borrowing is recorded to be insignificant for most of firm classifications
leading to inconclusive outcome. Inflation is having strong negative impact for
both manufacturing and entire sample. Higher inflation is leading to lesser
trade credit liability due to decline in real value of outstanding credit.
Significant Wald statistics indicate rejection of null of parameter values being
zero.
Table 2: Accounts receivable
Chemical Small Large
Variables All Manufacturing Services Product Textiles firms firms
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7)
Intercept -0.026** -0.031** 0.016 -0.03 -0.061** -0.009 -0.047
(0.012) (0.013) (0.034) (0.032) (0.026) (0.026) (0.034)
L1.Dep 0.554*** 0.535*** 0.507*** 0.371*** 0.431*** 0.397*** 0.643***
(0.018) (0.02) (0.052) (0.04) (0.042) (0.041) (0.034)
INV -0.014*** -0.016*** -0.009*** -0.016*** -0.021*** -0.014*** -0.005**
(0.001) (0.002) (0.003) (0.004) (0.003) (0.002) (0.003)
SIZE 0.021*** 0.023*** 0.014*** 0.032*** 0.03*** 0.019*** 0.016***
(0.002) (0.003) (0.005) (0.006) (0.005) (0.003) (0.005)
ROA 0.028*** 0.03*** 0.008 -0.033 0.1*** 0.005 0.049***
12 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9