Page 253 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 4
P. 253
STS583 Michael W. et al.
over any wrong MOS as well as the difference between the census and the
satellite based MOS will most likely develop further in favor of the latter MOS.
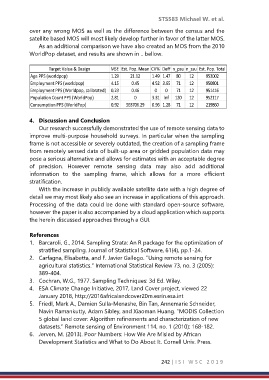
As an additional comparison we have also created an MOS from the 2010
WorldPop dataset, and results are shown in .. bellow.
Target Value & Design MSE Est. Pop. Mean CV% Deff n_psu n_ssu Est. Pop. Total
Age PPS (worldpop) 1.29 21.12 1.49 1.47 80 12 953002
Employment PPS (worldpop) 4.15 0.45 4.52 3.65 71 12 950801
Employment PPS (Worldpop, calibrated) 0.23 0.46 0 0 71 12 951416
Population Count PPS (WorldPop) 2.81 0 3.31 Inf 120 12 952117
Consumption PPS (WorldPop) 0.92 563706.29 0.96 1.28 71 12 219860
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Our research successfully demonstrated the use of remote sensing data to
improve multi-purpose household surveys. In particular when the sampling
frame is not accessible or severely outdated, the creation of a sampling frame
from remotely sensed data of built-up area or gridded population data may
pose a serious alternative and allows for estimates with an acceptable degree
of precision. However remote sensing data may also add additional
information to the sampling frame, which allows for a more efficient
stratification.
With the increase in publicly available satellite date with a high degree of
detail we may most likely also see an increase in applications of this approach.
Processing of the data could be done with standard open-source software,
however the paper is also accompanied by a cloud application which supports
the herein discussed approaches through a GUI.
References
1. Barcaroli, G., 2014. Sampling Strata: An R package for the optimization of
stratified sampling. Journal of Statistical Software, 61(4), pp.1-24.
2. Carfagna, Elisabetta, and F. Javier Gallego. "Using remote sensing for
agricultural statistics." International Statistical Review 73, no. 3 (2005):
389-404.
3. Cochran, W.G., 1977. Sampling Techniques: 3d Ed. Wiley.
4. ESA Climate Change Initiative, 2017, Land Cover project, viewed 22
January 2018, http://2016africalandcover20m.esrin.esa.int
5. Friedl, Mark A., Damien Sulla-Menashe, Bin Tan, Annemarie Schneider,
Navin Ramankutty, Adam Sibley, and Xiaoman Huang. "MODIS Collection
5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new
datasets." Remote sensing of Environment 114, no. 1 (2010): 168-182.
6. Jerven, M. (2013). Poor Numbers: How We Are Misled by African
Development Statistics and What to Do About It. Cornell Univ. Press.
242 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9