Page 225 - Special Topic Session (STS) - Volume 2
P. 225
STS486 R. Ayesha A. et al.
dioecious plants are generally preferred over monoecious plants (Zito et al.,
2016).
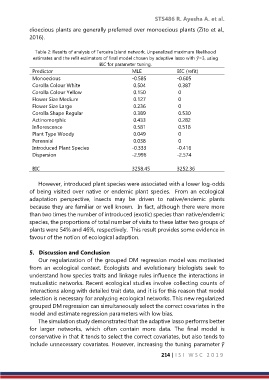
Table 2: Results of analysis of Terceira Island network. Unpenalized maximum likelihood
estimates and the refit estimators of final model chosen by adaptive lasso with ̃=3, using
BIC for parameter tuning.
Predictor MLE BIC (refit)
Monoecious -0.585 -0.605
Corolla Colour White 0.504 0.387
Corolla Colour Yellow 0.150 0
Flower Size Medium 0.127 0
Flower Size Large 0.236 0
Corolla Shape Regular 0.389 0.530
Actinomorphic 0.433 0.282
Inflorescence 0.581 0.518
Plant Type Woody 0.049 0
Perennial 0.038 0
Introduced Plant Species -0.333 -0.416
Dispersion -2.996 -2.574
BIC 3258.45 3252.36
However, introduced plant species were associated with a lower log-odds
of being visited over native or endemic plant species. From an ecological
adaptation perspective, insects may be driven to native/endemic plants
because they are familiar or well known. In fact, although there were more
than two times the number of introduced (exotic) species than native/endemic
species, the proportions of total number of visits to these latter two groups of
plants were 54% and 46%, respectively. This result provides some evidence in
favour of the notion of ecological adaption.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
Our regularization of the grouped DM regression model was motivated
from an ecological context. Ecologists and evolutionary biologists seek to
understand how species traits and linkage rules influence the interactions in
mutualistic networks. Recent ecological studies involve collecting counts of
interactions along with detailed trait data, and it is for this reason that model
selection is necessary for analyzing ecological networks. This new regularized
grouped DM regression can simultaneously select the correct covariates in the
model and estimate regression parameters with low bias.
The simulation study demonstrated that the adaptive lasso performs better
for larger networks, which often contain more data. The final model is
conservative in that it tends to select the correct covariates, but also tends to
include unnecessary covariates. However, increasing the tuning parameter ̃
214 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9