Page 170 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 2
P. 170
CPS1494 Senthilvel V. et al.
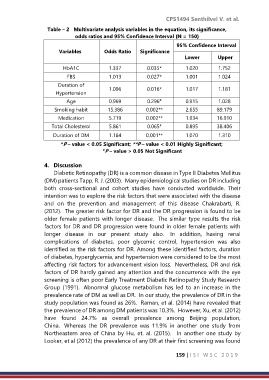
Table – 2 Multivariate analysis variables in the equation, its significance,
odds ratios and 95% Confidence Interval (N = 150)
95% Confidence Interval
Variables Odds Ratio Significance
Lower Upper
HbA1C 1.337 0.035* 1.020 1.752
FBS 1.013 0.027* 1.001 1.024
Duration of 1.096 0.016* 1.017 1.181
Hypertension
Age 0.969 0.296 # 0.915 1.028
Smoking habit 15.386 0.002** 2.655 89.179
Medication 5.719 0.002** 1.934 16.910
Total Cholesterol 5.861 0.065 # 0.895 38.406
Duration of DM 1.184 0.001** 1.070 1.310
*P – value < 0.05 Significant; **P – value < 0.01 Highly Significant;
# P – value > 0.05 Not Significant
4. Discussion
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a common disease in Type II Diabetes Mellitus
(DM) patients Tapp, R. J. (2003). Many epidemiological studies on DR including
both cross-sectional and cohort studies have conducted worldwide. Their
intention was to explore the risk factors that were associated with the disease
and on the prevention and management of this disease Chakrabarti, R.
(2012). The greater risk factor for DR and the DR progression is found to be
older female patients with longer disease. The similar type results the risk
factors for DR and DR progression were found in older female patients with
longer disease in our present study also. In addition, having renal
complications of diabetes, poor glycemic control, hypertension was also
identified as the risk factors for DR. Among these identified factors, duration
of diabetes, hyperglycemia, and hypertension were considered to be the most
affecting risk factors for advancement vision loss. Nevertheless, DR and risk
factors of DR hardly gained any attention and the concurrence with the eye
screening is often poor Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research
Group (1991). Abnormal glucose metabolism has led to an increase in the
prevalence rate of DM as well as DR. In our study, the prevalence of DR in the
study population was found as 26%. Raman, et al. (2014) have revealed that
the prevalence of DR among DM patients was 10.3%. However, Xu, et al. (2012)
have found 24.7% as overall prevalence among Beijing population,
China. Whereas the DR prevalence was 11.9% in another one study from
Northeastern area of China by Hu, et. al. (2015). In another one study by
Looker, et al (2012) the prevalence of any DR at their first screening was found
159 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9