Page 342 - Contributed Paper Session (CPS) - Volume 2
P. 342
CPS1878 Zakir H. et al.
2
Figure 7: Comparison of percent relative biases of ̂ and ̂ among normal, uniform
2
and t3 distributions.
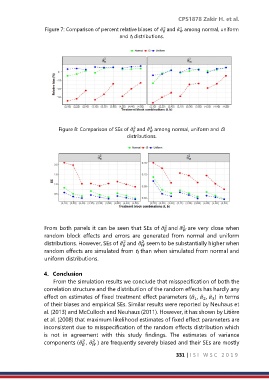
Figure 8: Comparison of SEs of ̂ and ̂ among normal, uniform and t3
2
2
distributions.
2
2
From both panels it can be seen that SEs of ̂ and ̂ are very close when
random block effects and errors are generated from normal and uniform
distributions. However, SEs of ̂ and ̂ seem to be substantially higher when
2
2
random effects are simulated from t3 than when simulated from normal and
uniform distributions.
4. Conclusion
From the simulation results we conclude that misspecification of both the
correlation structure and the distribution of the random effects has hardly any
effect on estimates of fixed treatment effect parameters (̂ , ̂ , ̂ ) in terms
2
1
3
of their biases and empirical SEs. Similar results were reported by Neuhaus et
al. (2013) and McCulloch and Neuhaus (2011). However, it has shown by Litière
et al. (2008) that maximum likelihood estimates of fixed effect parameters are
inconsistent due to misspecification of the random effects distribution which
is not in agreement with this study findings. The estimates of variance
2
2
components (̂ , ̂ ) are frequently severely biased and their SEs are mostly
331 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9