Page 403 - Invited Paper Session (IPS) - Volume 1
P. 403
IPS173 Yuki U.
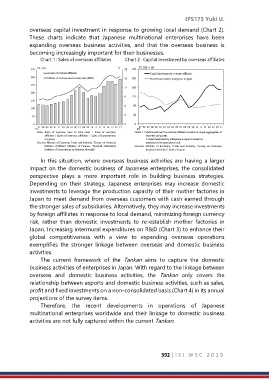
overseas capital investment in response to growing local demand (Chart 2).
These charts indicate that Japanese multinational enterprises have been
expanding overseas business activities, and that the overseas business is
becoming increasingly important for their businesses.
Chart 1 : Sales of overseas affiliates Chart 2 : Capital investment by overseas affiliates
Note: Ratio of overseas sales to total sales = Sales of overseas Notes: 1. Capital investment by overseas affiliates is based on simple aggregation of
affiliates / (Sales of overseas affiliates + Sales of corporations reported companies.
in Japan). 2. Fixed investment by enterprises in Japan is based on
Sources: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, “Survey on Overseas estimates of the population total.
Business Activities”; Ministry of Finance, “Financial Statements Sources: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, “Survey on Overseas
Statistics of Corporations by Industry, Annually” Business Activities”; Bank of Japan.
In this situation, where overseas business activities are having a larger
impact on the domestic business of Japanese enterprises, the consolidated
perspective plays a more important role in building business strategies.
Depending on their strategy, Japanese enterprises may increase domestic
investments to leverage the production capacity of their mother factories in
Japan to meet demand from overseas customers with cash earned through
the stronger sales of subsidiaries. Alternatively, they may increase investments
by foreign affiliates in response to local demand, minimizing foreign currency
risk, rather than domestic investments to re-establish mother factories in
Japan. Increasing intermural expenditures on R&D (Chart 3) to enhance their
global competitiveness with a view to expanding overseas operations
exemplifies the stronger linkage between overseas and domestic business
activities.
The current framework of the Tankan aims to capture the domestic
business activities of enterprises in Japan. With regard to the linkage between
overseas and domestic business activities, the Tankan only covers the
relationship between exports and domestic business activities, such as sales,
profit and fixed investments on a non-consolidated basis (Chart 4) in its annual
projections of the survey items.
Therefore, the recent developments in operations of Japanese
multinational enterprises worldwide and their linkage to domestic business
activities are not fully captured within the current Tankan.
392 | I S I W S C 2 0 1 9